Components
NativeBase is made from effective building blocks referred to as components. The Components are constructed in pure React Native platform along with some JavaScript functionality with rich set of customisable properties. These components allow you to quickly build the perfect interface.
NativeBase includes components such as anatomy of your app screens, header, textbox, buttons, badge, icon, form, checkbox, radio-button, list, card, thumbnail, progress bar, spinner, layout, search bar etc.
- Anatomy
- ActionSheet
- Badge
- Button
- Card
- Check Box
- Deck Swiper
- FABs
- Footer Tabs
- Form
- Header
- Icon
- Layout
- List
- Picker
- Radio Button
- Search Bar
- Segment
- Spinner
- Swipable List
- Tabs
- Thumbnail
- Toast
- Typography
- Drawer
- Ref
1. anatomy-headref
2. Anatomy
Automatically animates view to its new position.
A common way to use NativeBase screen structure is to have all the components within <Container>


General Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Header, Title, Content, Footer, FooterTab, Button, Left, Right, Body, Icon, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class AnatomyExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header>
<Left>
<Button transparent>
<Icon name='menu' />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body>
<Title>Header</Title>
</Body>
<Right />
</Header>
<Content>
<Text>
This is Content Section
</Text>
</Content>
<Footer>
<FooterTab>
<Button full>
<Text>Footer</Text>
</Button>
</FooterTab>
</Footer>
</Container>
);
}
}- NativeBase provides its own frame component, named after
<Container>. - All the components should be included within the Container.
- Container takes mainly three components:
<Header>,<Content>and<Footer>. - Container comes with its predefined stylesheet, with an added advantage of accepting user-defined styles.
- Usage of Container's
Headercomponent is very similar to your HTML <head>. So is withFooter. - The
Contentcomponent of Container is nothing but the body section of your screen.
Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Header | - | - | Renders as Header (navbar) of your screen. Input values: Button, Title (Text). |
| Content | - | - | Represents the main content of your screen. There can be only one <Content> component in a screen.
|
| Footer | - | - | Renders as Footer of your screen. Input values: FooterTab |
2.0.1. Header Anatomy
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Header, Title, Button, Left, Right, Body, Icon } from 'native-base';
export default class HeaderExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header>
<Left>
<Button transparent>
<Icon name='menu' />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body>
<Title>Header</Title>
</Body>
<Right />
</Header>
</Container>
);
}
}2.0.2. Content Anatomy
- This is a NativeBase component which renders as body element of your screen.
- Each screen can have only one
Contentcomponent and can be defined anywhere within the Container. - Content takes in the whole collection of React Native and NativeBase components.
- Content provides you with stylesheet.
- User can add custom styles while defining
Contentwithin their app. - Replacing Component: React Native Keyboard Aware Scroll View's KeyboardAwareScrollView
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Header, Content, Footer, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class ContentExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header />
<Content padder>
<Text>
This is Content Section
</Text>
</Content>
<Footer />
</Container>
);
}
}| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| padder | true | boolean | Applies margin at all sides to Content section. Can be used with NativeBase View as well. |
| disableKBDismissScroll | false | boolean | Disables automatic scroll on focus. |
| enableResetScrollToCoords | true | boolean | Lets the user enable or disable automatic resetScrollToCoords. |
2.0.3. Footer Anatomy
- NativeBase component that renders as footer, include your favourite apps for your screen.
- There can be only a single Footer component into your Container.
- To have Footer for your screen, include
Footercomponent withinContainer. - NativeBase gives you flexibility to define your Footer component anywhere in the bounds of Container.
- Footer takes input as: FooterTab.
- The components those are defined within
Footerwill be rendered in the same order that you define them. - Footer provides you with stylesheet.
- User can add custom styles while defining
Footerwithin their app. - Replacing Component: React Native View.
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Header, Content, Footer, FooterTab, Button, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class FooterExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header />
<Content />
<Footer>
<FooterTab>
<Button full>
<Text>Footer</Text>
</Button>
</FooterTab>
</Footer>
</Container>
);
}
}3. ActionSheet
NativeBase ActionSheet is a wrapper around the React Native ActionSheetIOS component.
For ActionSheet to work, you need to wrap your topmost component inside <Root> from native-base.
import { Root } from "native-base";
import { StackNavigator } from "react-navigation";
const AppNavigator = StackNavigator(
{
Page: { screen: Page },
}
);
export default () =>
<Root>
<AppNavigator />
</Root>;


General Syntax
import React, { Component } from "react";
import {
Container,
Header,
Left,
Button,
Body,
Title,
Icon,
Right,
Content,
ActionSheet,
Text
} from "native-base";
var BUTTONS = ["Option 0", "Option 1", "Option 2", "Delete", "Cancel"];
var DESTRUCTIVE_INDEX = 3;
var CANCEL_INDEX = 4;
export default class ActionSheetNB extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {};
}
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header>
<Left>
<Button
transparent
onPress={() => this.props.navigation.navigate("DrawerOpen")}
>
<Icon name="ios-menu" />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body>
<Title>ActionSheet</Title>
</Body>
<Right />
</Header>
<Content padder>
<Button
onPress={() =>
ActionSheet.show(
{
options: BUTTONS,
cancelButtonIndex: CANCEL_INDEX,
destructiveButtonIndex: DESTRUCTIVE_INDEX,
title: "Testing ActionSheet"
},
buttonIndex => {
this.setState({ clicked: BUTTONS[buttonIndex] });
}
)}
>
<Text>Actionsheet</Text>
</Button>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}
3.0.1. Icon ActionSheet (Android only)
Syntax for Icon ActionSheet
import React, { Component } from "react";
import {
Container,
Header,
Left,
Button,
Body,
Title,
Icon,
Right,
Content,
ActionSheet,
Text
} from "native-base";
var BUTTONS = [
{ text: "Option 0", icon: "american-football", iconColor: "#2c8ef4" },
{ text: "Option 1", icon: "analytics", iconColor: "#f42ced" },
{ text: "Option 2", icon: "aperture", iconColor: "#ea943b" },
{ text: "Delete", icon: "trash", iconColor: "#fa213b" },
{ text: "Cancel", icon: "close", iconColor: "#25de5b" }
];
var DESTRUCTIVE_INDEX = 3;
var CANCEL_INDEX = 4;
export default class ActionSheetNB extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {};
}
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header>
<Left>
<Button
transparent
onPress={() => this.props.navigation.navigate("DrawerOpen")}
>
<Icon name="ios-menu" />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body>
<Title>ActionSheet</Title>
</Body>
<Right />
</Header>
<Content padder>
<Button
onPress={() =>
ActionSheet.show(
{
options: BUTTONS,
cancelButtonIndex: CANCEL_INDEX,
destructiveButtonIndex: DESTRUCTIVE_INDEX,
title: "Testing ActionSheet"
},
buttonIndex => {
this.setState({ clicked: BUTTONS[buttonIndex] });
}
)}
>
<Text>Actionsheet</Text>
</Button>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}
iconColor is optional. Icons default to black.
Note: The use cases similar to RN's ActionSheetIOS.
4. Badge
All of us must have seen notification badges somewhere, such as on smart phones or facebook. NativeBase is here to include this into your collection of readymade components. Badges are numerical indicators of how many items are associated with an element. Badges can notify you that there are new or unread messages or notifications. These can be very effective in alerting the user to new things on your app.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Badge, Text, Icon } from 'native-base';
export default class BadgeExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Badge>
<Text>2</Text>
</Badge>
<Badge primary>
<Text>2</Text>
</Badge>
<Badge success>
<Text>2</Text>
</Badge>
<Badge info>
<Text>2</Text>
</Badge>
<Badge warning>
<Text>2</Text>
</Badge>
<Badge danger>
<Text>2</Text>
</Badge>
<Badge primary>
<Icon name="star" style={{ fontSize: 15, color: "#fff", lineHeight: 20 }}/>
</Badge>
<Badge style={{ backgroundColor: 'black' }}>
<Text style={{ color: 'white' }}>1866</Text>
</Badge>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}- NativeBase spectrum of colors are compatible with Badge.
Replacing Component: React Native View
Configuration
Property Default Option Description primary - boolean Add a blue background color to your component success - boolean Add a green background color to your component info - boolean Add a light blue background color to your component as shown warning - boolean Add a yellow warning background color to your component danger - boolean Add a red background color to your component
5. button-def-headref
6. Button
Button is a pure NativeBase component.
Buttons are the integral part of an application. They are used for various purposes like, submit or reset a form, navigate, performing interactive actions such as showing or hiding something in an app on click of the button, etc.


Contents:
- Button Theme
- Transparent Button
- Outline Button
- Rounded Button
- Block Button
- Full Button
- Icon Button
- Button Size
- Disabled Button
Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Button, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class ButtonExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
// NativeBase default style
<Button>
<Text>Click Me! </Text>
</Button>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Button, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class ButtonExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
// NativeBase default style
<Button>
<Text> Click Me! </Text>
</Button>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}- Supports React Native app on both iOS and Android devices.
- Button component takes input such as: Text, Icon, Text with Icon.
- NativeBase gives you privilege to customize the props of this component.
Example: To have custom style for button, include them instyleprop of button. - Intakes user-defined styles.
- NativeBase has provided its users with enormous list of
propsthat can be used with Button. - Replacing Component:
- React Native TouchableOpacity for iOS
- React Native TouchableNativeFeedback for Android
Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| style | - | - | Defines button style |
| active | - | boolean | Boolean value to describe state of Button |
| transparent | true | boolean | Renders child element of button |
| bordered | - | - | Applies outline button style. |
| rounded | - | - | Renders button with slightly round shaped edges |
| block | - | - | Block level button |
| full | - | - | Full width button |
| disabled | true | boolean | Disables click option for button |
| small | - | - | For small size button |
| large | - | - | For large size button |
| iconRight | - | - | Right Padding for the icon |
| iconLeft | - | - | Left Padding for the icon. |
| light | - | boolean | Add a light white background color to your component. |
| primary | - | boolean | Add a blue background color to your component |
| success | - | boolean | Add a green background color to your component |
| info | - | boolean | Add a light blue background color to your component as shown |
| warning | - | boolean | Add a yellow warning background color to your component |
| danger | - | boolean | Add a red background color to your component |
| dark | - | boolean | Add a black background color to your component |
7. button-theme-headref
7.0.1. Button Theme
NativeBase provides button with wide range of colors, size and various other props.
NativeBase provides following color themes:
- Primary (default)
- Success
- Info
- Warning
- Danger
- Light
- Dark


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Button, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class ButtonThemeExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Button light><Text> Light </Text></Button>
<Button primary><Text> Primary </Text></Button>
<Button success><Text> Success </Text></Button>
<Button info><Text> Info </Text></Button>
<Button warning><Text> Warning </Text></Button>
<Button danger><Text> Danger </Text></Button>
<Button dark><Text> Dark </Text></Button>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}8. button-transparent-headref
8.0.1. Transparent Button
Include transparent prop with Button. This will render button without border and background color.

 Syntax
Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Button, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class TransparentButtonExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Button transparent light>
<Text>Light</Text>
</Button>
<Button transparent>
<Text>Primary</Text>
</Button>
<Button transparent success>
<Text>Success</Text>
</Button>
<Button transparent info>
<Text>Info</Text>
</Button>
<Button transparent warning>
<Text>Warning</Text>
</Button>
<Button transparent danger>
<Text>Danger</Text>
</Button>
<Button transparent dark>
<Text>Dark</Text>
</Button>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}9. button-outline-headref
9.0.1. Outline Button
Include bordered prop with Button to apply outline button style.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Button, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class OutlineButtonExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Button bordered light>
<Text>Light</Text>
</Button>
<Button bordered>
<Text>Primary</Text>
</Button>
<Button bordered success>
<Text>Success</Text>
</Button>
<Button bordered info>
<Text>Info</Text>
</Button>
<Button bordered warning>
<Text>Warning</Text>
</Button>
<Button bordered danger>
<Text>Danger</Text>
</Button>
<Button bordered dark>
<Text>Dark</Text>
</Button>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}10. button-rounded-headref
10.0.1. Rounded Button
Include rounded prop with Button to easily style your buttons.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Button, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class RoundedButtonExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Button rounded light>
<Text>Light</Text>
</Button>
<Button rounded>
<Text>Primary</Text>
</Button>
<Button rounded success>
<Text>Success</Text>
</Button>
<Button rounded info>
<Text>Info</Text>
</Button>
<Button rounded warning>
<Text>Warning</Text>
</Button>
<Button rounded danger>
<Text>Danger</Text>
</Button>
<Button rounded dark>
<Text>Dark</Text>
</Button>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}11. button-block-headref
11.0.1. Block Button
A block level button spans the entire width of the parent element.
Create block level buttons by adding block prop with the Button


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Button, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class BlockButtonExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Button block light>
<Text>Light</Text>
</Button>
<Button block>
<Text>Primary</Text>
</Button>
<Button block success>
<Text>Success</Text>
</Button>
<Button block info>
<Text>Info</Text>
</Button>
<Button block warning>
<Text>Warning</Text>
</Button>
<Button block danger>
<Text>Danger</Text>
</Button>
<Button block dark>
<Text>Dark</Text>
</Button>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}12. button-full-headref
12.0.1. Full Button
Adding full to a button will make the button take 100% of its parent’s width. However, it will also remove the button’s left and right borders. This style is useful when the button should stretch across the entire width of the display.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Button, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class FullButtonExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Button full light>
<Text>Light</Text>
</Button>
<Button full>
<Text>Primary</Text>
</Button>
<Button full success>
<Text>Success</Text>
</Button>
<Button full info>
<Text>Info</Text>
</Button>
<Button full warning>
<Text>Warning</Text>
</Button>
<Button full danger>
<Text>Danger</Text>
</Button>
<Button full dark>
<Text>Dark</Text>
</Button>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}13. button-icon-headref
13.0.1. Icon Button
The Icon Buttons, can take text and/or icon as child elements inside the Button.
This goes as simple as this: include your choice of icon using Icon component within the Button component.
![]()
![]()
Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Button, Icon, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class IconButtonExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Button iconLeft light>
<Icon name='arrow-back' />
<Text>Back</Text>
</Button>
<Button iconRight light>
<Text>Next</Text>
<Icon name='arrow-forward' />
</Button>
<Button iconLeft>
<Icon name='home' />
<Text>Home</Text>
</Button>
<Button iconLeft transparent primary>
<Icon name='beer' />
<Text>Pub</Text>
</Button>
<Button iconLeft dark>
<Icon name='cog' />
<Text>Settings</Text>
</Button>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}14. button-size-headref
14.0.1. Button Size
Want to have buttons of fancy size?
Include the following props with your Button.
small: for small size button.large: for large size button.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Button, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class ButtonSizeExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
//Small size button
<Button small primary>
<Text>Default Small</Text>
</Button>
//Regular size button
<Button success>
<Text>Success Default</Text>
</Button>
//Large size button
<Button large dark>
<Text>Dark Large</Text>
</Button>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}15. button-disabled-headref
15.0.1. Disabled Button
A disabled button is unusable and un-clickable.
The disabled prop of NativeBase Button is of type boolean. When present, it specifies that the button should be disabled. The disabled prop can be set to keep a user from clicking on the button until some other condition has been met (like selecting a checkbox, etc.). Then, a conditional code could remove the disabled value, and make the button usable.

 Syntax
Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Button, Text, Icon } from 'native-base';
export default class DisabledButtonExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Button disabled><Text>Default</Text></Button>
<Button disabled bordered><Text>Bordered</Text></Button>
<Button disabled rounded><Text>Rounded</Text></Button>
<Button disabled large><Text>Large</Text></Button>
<Button disabled iconRight>
<Text>Icon Button</Text>
<Icon name="home" />
</Button>
<Button disabled block><Text>Block</Text></Button>
<Button disabled full><Text>Full</Text></Button>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}16. card-def-headref
17. Card
Card is a pure NativeBase component.
Card is a flexible and extensible content container. It includes options for headers and footers, a wide variety of content, contextual background colors, and powerful display options.
NativeBase Cards support a wide variety of content, including images, text, list groups, links, and more. Mix and match multiple content types to create the card you need.


Contents:
Genertal Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Card, CardItem, Body, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class CardExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Card>
<CardItem>
<Body>
<Text>
//Your text here
</Text>
</Body>
</CardItem>
</Card>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}- Card
- This component adds a box-shadow by default.
- Also provides default spacing and alignment between cards.
- CardItem
- This is the child component of
Card. - Works very similar to the list items of list.
- Takes input such as: Text, Button, Image, Thumbnail, Icon.
- Card takes any number of CardItem.
- This is the child component of
- Replacing Component
- React Native View for Card
- React Native TouchableOpacity / View for CardItem
Configuration for Card
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| transparent | - | - | Removes card shadow from iOS and elevation from android |
| dataArray | Array | user-defined array | Array of data chunks to render iteratively. |
| renderRow | Function | - | Callback which takes a chunk of data from dataArray and returns as a component. |
Configuration for CardItem
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| header | - | - | Displays text as header for cards |
| cardBody | - | - | Defines section for body of card. The child components are rendered with proper spacing and alignment. |
| footer | - | - | Displays text as footer for cards |
| button | - | - | To navigate on click of a card item. |
| bordered | false | boolean | To add border to the cardItems |
18. card-headfoot-headref
18.0.1. Card Header and Footer
To add an optional header and/or footer within a card, include header prop with the CardItem.
- Card Header: Include
headerprop with first instance of CardItem within Card. - Card Footer: Include
footerprop with last instance of CardItem within Card.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Card, CardItem, Text, Body } from 'native-base';
export default class CardHeaderFooterExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Card>
<CardItem header>
<Text>NativeBase</Text>
</CardItem>
<CardItem>
<Body>
<Text>
//Your text here
</Text>
</Body>
</CardItem>
<CardItem footer>
<Text>GeekyAnts</Text>
</CardItem>
</Card>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}19. card-list-headref
19.0.1. Card List
Include CardItem subsequently within Card to create a card with lists.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Card, CardItem, Text, Icon, Right } from 'native-base';
export default class CardListExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Card>
<CardItem>
<Icon active name="logo-googleplus" />
<Text>Google Plus</Text>
<Right>
<Icon name="arrow-forward" />
</Right>
</CardItem>
</Card>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}20. card-image-headref
20.0.1. Card Image
Want to have something more with Card Lists?
Include image with CardItem within Card along with some text before and after image to create a card with lists.
Here is your Card Image ready !


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Image } from 'react-native';
import { Container, Content, Card, CardItem, Thumbnail, Text, Button, Icon, Left, Body, Right } from 'native-base';
export default class CardImageExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Card>
<CardItem>
<Left>
<Thumbnail source={{uri: 'Image URL'}} />
<Body>
<Text>NativeBase</Text>
<Text note>GeekyAnts</Text>
</Body>
</Left>
</CardItem>
<CardItem cardBody>
<Image source={{uri: 'Image URL'}} style={{height: 200, width: null, flex: 1}}/>
</CardItem>
<CardItem>
<Left>
<Button transparent>
<Icon active name="thumbs-up" />
<Text>12 Likes</Text>
</Button>
</Left>
<Body>
<Button transparent>
<Icon active name="chatbubbles" />
<Text>4 Comments</Text>
</Button>
</Body>
<Right>
<Text>11h ago</Text>
</Right>
</CardItem>
</Card>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}21. card-showcase-headref
21.0.1. Card Showcase
Card Showcase is further customization of Card Image. It uses several different items.
- Begins with the Card List component, which is similar to our List Avatar.
- Make use of Left, Body and Right components to align the content of your Card header.
- To mixup Image with other NativeBase components in a single CardItem, include the content within Body component.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Image } from 'react-native';
import { Container, Content, Card, CardItem, Thumbnail, Text, Button, Icon, Left, Body } from 'native-base';
export default class CardShowcaseExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Card style={{flex: 0}}>
<CardItem>
<Left>
<Thumbnail source={{uri: 'Image URL'}} />
<Body>
<Text>NativeBase</Text>
<Text note>April 15, 2016</Text>
</Body>
</Left>
</CardItem>
<CardItem>
<Body>
<Image source={{uri: 'Image URL'}} style={{height: 200, width: 200, flex: 1}}/>
<Text>
//Your text here
</Text>
</Body>
</CardItem>
<CardItem>
<Left>
<Button transparent textStyle={{color: '#87838B'}}>
<Icon name="logo-github" />
<Text>1,926 stars</Text>
</Button>
</Left>
</CardItem>
</Card>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}22. checkbox-headref
23. Check Box
Check Box allows the user to select a number of items from a set of choices.
Replacing Component: React Native TouchableOpacity


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, ListItem, CheckBox, Text, Body } from 'native-base';
export default class CheckBoxExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<ListItem>
<CheckBox checked={true} />
<Body>
<Text>Daily Stand Up</Text>
</Body>
</ListItem>
<ListItem>
<CheckBox checked={false} />
<Body>
<Text>Discussion with Client</Text>
</Body>
</ListItem>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| checked | false | boolean | Represents the state value of an item from set of choices. |
| color | - | user-defined | Background color of checkbox |
| onPress | - | - | Handler to be called when the user selects / unselects the checkbox |
24. deckswiper-headref
25. Deck Swiper
Looking at data one piece at a time is more efficient when you consider people you might want to date, restaurants, streaming music, or local events you might want to check out.
NativeBase Deck Swiper helps you evaluate one option at a time, instead of selecting from a set of options.
Replacing Component: React Native View


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Image } from 'react-native';
import { Container, View, DeckSwiper, Card, CardItem, Thumbnail, Text, Left, Body, Icon } from 'native-base';
const cards = [
{
text: 'Card One',
name: 'One',
image: require('./img/swiper-1.png'),
},
. . .
];
export default class DeckSwiperExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<View>
<DeckSwiper
dataSource={cards}
renderItem={item =>
<Card style={{ elevation: 3 }}>
<CardItem>
<Left>
<Thumbnail source={item.image} />
<Body>
<Text>{item.text}</Text>
<Text note>NativeBase</Text>
</Body>
</Left>
</CardItem>
<CardItem cardBody>
<Image style={{ height: 300, flex: 1 }} source={item.image} />
</CardItem>
<CardItem>
<Icon name="heart" style={{ color: '#ED4A6A' }} />
<Text>{item.name}</Text>
</CardItem>
</Card>
}
/>
</View>
</Container>
);
}
}Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| dataSource | - | User defined object | Chunk of data(object) |
| renderEmpty | Function | - | Callback that is called when all the cards are swiped and dataSource is empty and returns a component. |
| renderItem | Function | - | Callback which takes a chunk of data and returns a component. |
| renderTop | Function | - | Callback which takes a chunk of data and returns top layer component. |
| renderBottom | Function | - | Callback which takes a chunk of data and returns bottom layer component. |
| looping | true | boolean | Loop through the data |
| onSwipeRight | Function | - | Callback that is called when the Card is swiped Right |
| onSwipeLeft | Function | - | Callback that is called when the Card is swiped Left |
26. adv-deckswiper-def-headref
26.0.1. Advanced Deck Swiper
Swipe Deck with callback function.
Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Image } from 'react-native';
import { Container, View, DeckSwiper, Card, CardItem, Thumbnail, Text, Left, Body, Icon } from 'native-base';
const cards = [
{
text: 'Card One',
name: 'One',
image: require('./img/swiper-1.png'),
},
. . .
];
export default class DeckSwiperExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<View>
<DeckSwiper
ref={(c) => this._deckSwiper = c}
dataSource={cards}
renderEmpty={() =>
<View style={{ alignSelf: "center" }}>
<Text>Over</Text>
</View>
renderItem={item =>
<Card style={{ elevation: 3 }}>
<CardItem>
<Left>
<Thumbnail source={item.image} />
<Body>
<Text>{item.text}</Text>
<Text note>NativeBase</Text>
</Body>
</Left>
</CardItem>
<CardItem cardBody>
<Image style={{ height: 300, flex: 1 }} source={item.image} />
</CardItem>
<CardItem>
<Icon name="heart" style={{ color: '#ED4A6A' }} />
<Text>{item.name}</Text>
</CardItem>
</Card>
}
/>
</View>
<View style={{ flexDirection: "row", flex: 1, position: "absolute", bottom: 50, left: 0, right: 0, justifyContent: 'space-between', padding: 15 }}>
<Button iconLeft onPress={() => this._deckSwiper._root.swipeLeft()}>
<Icon name="arrow-back" />
<Text>Swipe Left</Text>
</Button>
<Button iconRight onPress={() => this._deckSwiper._root.swipeRight()}>
<Icon name="arrow-forward" />
<Text>Swipe Right</Text>
</Button>
</View>
</Container>
);
}
}27. fabs-def-headref
28. FABs
FABs (Floating Action Buttons) are used for a special type of promoted action. They are distinguished by a circled icon floating above the UI in a fixed position and have special motion behaviors. When clicked, it may contain more related actions.
Replacing Component: React Native Animated


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, View, Button, Icon, Fab } from 'native-base';
export default class FABExample extends Component {
constructor() {
this.state = {
active: 'true'
};
}
render() {
return (
<Container>
<View style={{ flex: 1 }}>
<Fab
active={this.state.active}
direction="up"
containerStyle={{ }}
style={{ backgroundColor: '#5067FF' }}
position="bottomRight"
onPress={() => this.setState({ active: !this.state.active })}>
<Icon name="share" />
<Button style={{ backgroundColor: '#34A34F' }}>
<Icon name="logo-whatsapp" />
</Button>
<Button style={{ backgroundColor: '#3B5998' }}>
<Icon name="logo-facebook" />
</Button>
<Button disabled style={{ backgroundColor: '#DD5144' }}>
<Icon name="mail" />
</Button>
</Fab>
</View>
</Container>
);
}
}Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| active | true | boolean | Toggle status of FAB |
| direction | up | up, down, left, right | Direction of Buttons that popup on click of FAB. |
| position | bottomRight |
topLeft, topRight bottomLeft, bottomRight |
Position of FAB on screen. |
| containerStyle | - | user-defined | Padding options to render FAB. |
| style | - | user-defined | User defined styles. |
29. fabs-multiple-headref
29.0.1. Multiple FABs


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, View, Fab, Button, Icon } from 'native-base';
export default class FABExample extends Component {
constructor() {
this.state = {
active: 'true'
};
}
render() {
return (
<Container>
<View style={{ flex: 1 }}>
<Fab
active={this.state.active}
direction="up"
containerStyle={{ }}
style={{ backgroundColor: '#5067FF' }}
position="bottomRight"
onPress={() => this.setState({ active: !this.state.active })}>
....
</Fab>
<Fab direction="left" position="topRight">
....
</Fab>
<Fab direction="down" position="topLeft">
....
</Fab>
<Fab direction="right" position="bottomLeft">
....
</Fab>
</View>
</Container>
);
}
}30. footer-tabs-headref
31. Footer Tabs
Tabs are a horizontal region of buttons or links that allow for a consistent navigation experience between screens. It can contain any combination of text and icons, and is a popular method for enabling mobile navigation.
Replacing Component: React Native View
Contents


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Footer, FooterTab, Button, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class FooterTabsExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content />
<Footer>
<FooterTab>
<Button>
<Text>Apps</Text>
</Button>
<Button>
<Text>Camera</Text>
</Button>
<Button active>
<Text>Navigate</Text>
</Button>
<Button>
<Text>Contact</Text>
</Button>
</FooterTab>
</Footer>
</Container>
);
}
}Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| active | true | boolean | This is Button prop (applicable with FooterTab only). Sets a Footer Button active. |
| badge | true | boolean | This is Button prop (applicable with FooterTab only). Set to true if using Badges. |
| vertical | true | boolean | This is Button prop (applicable with FooterTab only). Use this prop to vertically align footer elements like icons and text. Necessary when using Badge in Footer Tabs. |
32. footer-icon-headref
32.0.1. Icon Footer
![]()
![]()
Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Footer, FooterTab, Button, Icon } from 'native-base';
export default class IconFooterTabsExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content />
<Footer>
<FooterTab>
<Button>
<Icon name="apps" />
</Button>
<Button>
<Icon name="camera" />
</Button>
<Button active>
<Icon active name="navigate" />
</Button>
<Button>
<Icon name="person" />
</Button>
</FooterTab>
</Footer>
</Container>
);
}
}33. footer-text-headref
33.0.1. Icon Footer with Text
![]()
![]()
Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Footer, FooterTab, Button, Icon, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class IconTextFooterTabsExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content />
<Footer>
<FooterTab>
<Button vertical>
<Icon name="apps" />
<Text>Apps</Text>
</Button>
<Button vertical>
<Icon name="camera" />
<Text>Camera</Text>
</Button>
<Button vertical active>
<Icon active name="navigate" />
<Text>Navigate</Text>
</Button>
<Button vertical>
<Icon name="person" />
<Text>Contact</Text>
</Button>
</FooterTab>
</Footer>
</Container>
);
}
}34. footer-badge-headref
34.0.1. Footer with badge


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Footer, FooterTab, Button, Icon, Text, Badge } from 'native-base';
export default class BadgeFooterTabsExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content />
<Footer>
<FooterTab>
<Button badge vertical>
<Badge><Text>2</Text></Badge>
<Icon name="apps" />
<Text>Apps</Text>
</Button>
<Button vertical>
<Icon name="camera" />
<Text>Camera</Text>
</Button>
<Button active badge vertical>
<Badge ><Text>51</Text></Badge>
<Icon active name="navigate" />
<Text>Navigate</Text>
</Button>
<Button vertical>
<Icon name="person" />
<Text>Contact</Text>
</Button>
</FooterTab>
</Footer>
</Container>
);
}
}35. Form
NativeBase makes use of List to design Forms that include group of related input components. Include any combination of NativeBase components to make up your form.
Input is a NativeBase component built on top of React Native's TextInput. Item component is wrap around it apply the specific styles.
A foundational component for inputting text into the app via a keyboard. Props provide configurability for several features, such as auto-correction, auto-capitalization, placeholder text, and different keyboard types, such as a numeric keypad.
Provides a number of attributes that follows styling and interaction guidelines for each platform, so that they are intuitive for users to interact with.
Replacing Component:
- Form: React Native View
- Item: React Native TouchableOpacity
- Input: React Native TextInput
- Label: React Native Text
Contents:
- Fixed Label
- Inline Label
- Floating Label
- Stacked Label
- Regular Textbox
- Underlined Textbox
- Rounded Textbox
- Icon Textbox
- Success Input Textbox
- Error Input Textbox
- Disabled Textbox


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Form, Item, Input } from 'native-base';
export default class FormExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Form>
<Item>
<Input placeholder="Username" />
</Item>
<Item last>
<Input placeholder="Password" />
</Item>
</Form>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| fixedLabel | true | boolean | Label is Fixed to the left of the Input and does not hide when text is entered. |
| floatingLabel | true | boolean | Label that animates upwards when the input is selected and animates downward when input is erased. |
| inlineLabel | - | boolean | Label placed to the left of the input element. When the user enters text, the label does not hide. This can also be used along with placeholder. |
| stackedLabel | - | - | Places the label on top of the input element which appears like a stack. This can also be used along with placeholder. |
| bordered | - | - | Includes border with the textbox. |
| rounded | - | - | Includes rounded border with the textbox. |
| underline | true | - | Includes and underline border with the textbox. |
| disabled | - | - | Disables inputting data. |
| placeholderLabel | - | - | Renders the same way the TextInput does with the form styling of NativeBase. |
| placeholder | - | - | The string that will be rendered before text input has been entered. Optional user-defined placeholder for textbox. |
| last | - | - | Style the Form Item for the last Item of the Form. |
| error | - | - | The border color of textbox for invalid input. |
| success | - | - | The border color of textbox for valid input. |
Note: Form in NativeBase is just a wrapper around the inputs and hence has no onSubmit function.
36. fixed-label-headref
36.0.1. Fixed Label
The fixedLabel property creates an Input component, whose Label is fixed at the left of the Input, which does not hide when text is entered. The input aligns on the same position, regardless of the length of the label. It can be used with placeholder as well.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Form, Item, Input, Label } from 'native-base';
export default class FixedLabelExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Form>
<Item fixedLabel>
<Label>Username</Label>
<Input />
</Item>
<Item fixedLabel last>
<Label>Password</Label>
<Input />
</Item>
</Form>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}37. inline-label-headref
37.0.1. Inline Label
The inlineLabel property creates an Input component, whose Label is in-line with Input, which does not hide when text is entered. It can be used with placeholder as well.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Form, Item, Input, Label } from 'native-base';
export default class InlineLabelExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Form>
<Item inlineLabel>
<Label>Username</Label>
<Input />
</Item>
<Item inlineLabel last>
<Label>Password</Label>
<Input />
</Item>
</Form>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}38. floating-label-headref
38.0.1. Floating Label
The floatingLabel property creates an Input component, whose Label animates upward when the input is selected and animates downward when input is erased.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Form, Item, Input, Label } from 'native-base';
export default class FloatingLabelExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Form>
<Item floatingLabel>
<Label>Username</Label>
<Input />
</Item>
<Item floatingLabel last>
<Label>Password</Label>
<Input />
</Item>
</Form>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}39. stacked-label-headref
39.0.1. Stacked Label
The stackedLabel property creates an Input component that places the label on top of input element which appears like a stack. This can also be used along with placeholder.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Form, Item, Input, Label } from 'native-base';
export default class StackedLabelExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Form>
<Item stackedLabel>
<Label>Username</Label>
<Input />
</Item>
<Item stackedLabel last>
<Label>Password</Label>
<Input />
</Item>
</Form>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}40. regular-textbox-headref
40.0.1. Regular Textbox
To use the regular textbox which is rectangular in shape, include the regular prop with Item.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Input, Item } from 'native-base';
export default class RegularTextboxExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Item regular>
<Input placeholder='Regular Textbox' />
</Item>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}41. underlined-textbox-headref
41.0.1. Underlined Textbox
To use the underlined textbox, include the underline prop with Item.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Item, Input } from 'native-base';
export default class UnderlinedTextboxExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Item>
<Input placeholder="Underline Textbox" />
</Item>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}42. rounded-textbox-headref
42.0.1. Rounded Textbox
To have a textbox with round type border, include the rounded prop with Item.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Item, Input } from 'native-base';
export default class RoundedTextboxExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Item rounded>
<Input placeholder='Rounded Textbox'/>
</Item>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}43. icon-textbox-headref
43.0.1. Icon Textbox
Icons can be easily added to the NativeBase Textbox. To do so, include an icon within the <Item>.
The icons render in the order of its definition within Item.
![]()
![]()
Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Item, Input, Icon } from 'native-base';
export default class IconTextboxExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
// Text input box with icon aligned to the left
<Item>
<Icon active name='home' />
<Input placeholder='Icon Textbox'/>
</Item>
// Text input box with icon aligned to the right
<Item>
<Input placeholder='Icon Alignment in Textbox'/>
<Icon active name='swap' />
</Item>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}44. success-textbox-headref
44.0.1. Success Input Textbox
To display textbox with valid data, include the success prop with Item.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Item, Input, Icon } from 'native-base';
export default class SuccessInputTextboxExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Item success>
<Input placeholder='Textbox with Success Input'/>
<Icon name='checkmark-circle' />
</Item>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}45. error-textbox-headref
45.0.1. Error Input Textbox
To display textbox with invalid data, include the error prop with Item.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Item, Input, Icon } from 'native-base';
export default class ErrorInputTextboxExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Item error>
<Input placeholder='Textbox with Error Input'/>
<Icon name='close-circle' />
</Item>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}46. disabled-textbox-headref
46.0.1. Disabled Textbox
To restrict inputting data into textbox, include the disabled prop with Item and Input.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Item, Input, Icon } from 'native-base';
export default class DisabledTextboxExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Item disabled>
<Input disabled placeholder='Disabled Textbox'/>
<Icon name='information-circle' />
</Item>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}47. header-def-headref
48. Header
- NativeBase component that renders as Header (navbar) for your screen.
- There can be a single Header component into your Container.
- To have Header for your screen, include
Headercomponent withinContainer. - Header takes input as:
Left,BodyandRight. - The components those are defined within
Headerwill be rendered in the same order that you define them. - Header provides you with stylesheet.
- User can add custom styles while defining
Headerwithin their app. - Replacing Component: React Native View

![]()
Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Header, Left, Body, Right, Button, Icon, Title } from 'native-base';
export default class HeaderExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header>
<Left>
<Button transparent>
<Icon name='arrow-back' />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body>
<Title>Header</Title>
</Body>
<Right>
<Button transparent>
<Icon name='menu' />
</Button>
</Right>
</Header>
</Container>
);
}
}Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Left | - | - | Components render to the left in Header |
| Body | - | - | Components render at the center of Header |
| Right | - | - | Components render to the right in Header |
| iosBarStyle | - | 'light-content', 'dark-content' or 'default' | Set iOS barStyle |
| androidStatusBarColor | - | - | Set bakground color for status bar in android |
| backgroundColor | - | string | Set background color |
| noShadow | - | boolean | Removes elevation from android |
| searchBar | - | boolean | Add searchBar to header or not |
| rounded | - | boolean | Make Header searchBar Rounded |
| hasSubtitle | - | boolean | Add subtitle to the Header Component |
| hasSegment | - | boolean | Add Segments to Header Component |
| hasTabs | - | boolean | Add Tabs to Header Component |
48.0.1. Header with only title
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Header, Left, Body, Right, Title } from 'native-base';
export default class HeaderTitleExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header>
<Left/>
<Body>
<Title>Header</Title>
</Body>
<Right />
</Header>
</Container>
);
}
}48.0.2. Header with Icon and Text Buttons
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Header, Left, Body, Right, Button, Icon, Title, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class HeaderIconTextExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header>
<Left>
<Button transparent>
<Icon name='arrow-back' />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body>
<Title>Header</Title>
</Body>
<Right>
<Button transparent>
<Text>Cancel</Text>
</Button>
</Right>
</Header>
</Container>
);
}
}48.0.3. Header with Title and Subtitle
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Header, Left, Body, Right, Button, Icon, Title, Subtitle } from 'native-base';
export default class HeaderTitleSubtitleExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header>
<Left>
<Button transparent>
<Icon name='arrow-back' />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body>
<Title>Title</Title>
<Subtitle>Subtitle</Subtitle>
</Body>
<Right />
</Header>
</Container>
);
}
}49. icon-def-headref
50. Icon
Perfect, crisp, high definition icons and pixel ideal fonts powered by NativeBase to preserve matters very high first-rate. You will continually have pixel perfect icons on your initiatives.
Uses Ionicons from React Native Vector Icons
![]()
![]()
Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Icon } from 'native-base';
export default class IconExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Icon name='home' />
<Icon ios='ios-menu' android="md-menu" style={{fontSize: 20, color: 'red'}}/>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}Iconcan take any two of the following attributes: name, ios, android.- In case if you want to include icon with custom color, size etc then that should go into
style. - All the icons in the icon libraries of NativeBase, are scalable vector icons that can be customized in terms of size, color, etc.
Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | - | - | Name of the icon. |
| ios | - | - | Name of the icon for iOS devices. |
| android | - | - | Name of the icon for Android devices. |
| active | default | boolean | Renders filled icons. By default renders outline icon. |
| color | black | user-defined |
Renders icon with defined color. Include this prop within style
|
| fontSize | 27 | user-defined |
Renders icon with defined icon-size. Include this prop within style
|
51. Layout
The layout system is an essential concept that needs to be mastered in order to create great layouts and UIs. React Native uses Flexbox to create the layouts, which is great when we need to accommodate our components and views in different screen sizes or even different devices. Flexbox is awesome but it could be tiresome for newbies.
Not being very good at Flexbox?
Here comes the Easy Grid of NativeBase, a wrapper of Flexbox.
The layout system in NativeBase is very powerful and flexible. No more worries about props of Flexbox such as alignItems, flexDirection, justifyContent, margin, padding, position, width etc. You can create any layout with all the available options that we have. In order to build custom layouts and components, understanding how layout works in NativeBase is not as hard as Flexbox.
Flexbox makes it look like percentages, however what actually is happening is just ratios. On the easier part, ratios are easier to represent than percentage / decimals. For this reason, the Easy Grid takes in ratios in place of percentage.
Performance wise, Easy Grid is noteworthy and works as fine as Flexbox, not much of calculation.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content } from 'native-base';
import { Col, Row, Grid } from 'react-native-easy-grid';
export default class LayoutExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Grid>
<Col style={{ backgroundColor: '#635DB7', height: 200 }}></Col>
<Col style={{ backgroundColor: '#00CE9F', height: 200 }}></Col>
</Grid>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}NOTE: <Content> component uses <ScrollView>. This is required by <Col> and <Row> elements of Easy-Grid to have a defined height.
Replacing Component for Grid, Col, Row: React Native View
52. list-def-headref
53. List
This component is completely built by NativeBase.
A base component for specifying lists of information. List must contain one or more list elements. Props provide configurability for several features. Provides a number of attributes that follows styling and interaction guidelines for each platform, so that they are intuitive for users to interact with.


Contents:
Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, List, ListItem, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class ListExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<List>
<ListItem>
<Text>Simon Mignolet</Text>
</ListItem>
<ListItem>
<Text>Nathaniel Clyne</Text>
</ListItem>
<ListItem>
<Text>Dejan Lovren</Text>
</ListItem>
</List>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}
List: This component defines a section to include your list items.ListItem:- This is the child component of
List. - Defines a list item.
- Adds border at bottom of each ListItem.
- List takes any number of ListItem.
- Takes input such as: Text, Badge, Thumbnail, Icon. Replacing Component
- This is the child component of
- List: React Native View
- ListItem:
- React Native TouchableOpacity for iOS
- React Native TouchableNativeFeedback for Android
Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| button | - | boolean | To navigate on click of a list item. |
| dataArray | Array | user-defined array | Array of data chunks to render iteratively. |
| itemDivider | - | boolean | Helps to organize and group the list items. |
| itemHeader | - | - | Style the item as the header for the ListItems. |
| first | - | - | Adds style of first ListItem. |
| last | - | - | Adds style of last ListItem. |
| icon | - | - | To have list styling of icons . |
| avatar | - | - | Style the list to have Avatars. |
| thumbnail | - | - | Style the list to have Thumbnails. |
| renderRow | Function | - | Callback which takes a chunk of data from dataArray and returns as a component. |
54. list-divider-headref
54.0.1. List Divider
The List Divider component creates a list separator, which can be used for grouping list items. To create a divider for any child element of the list, include itemDivider prop with ListItem component.
The List Divider of NativeBase comes with default style which is easily customisable.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, List, ListItem, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class ListDividerExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<List>
<ListItem itemDivider>
<Text>A</Text>
</ListItem>
<ListItem >
<Text>Aaron Bennet</Text>
</ListItem>
<ListItem>
<Text>Ali Connors</Text>
</ListItem>
<ListItem itemDivider>
<Text>B</Text>
</ListItem>
<ListItem>
<Text>Bradley Horowitz</Text>
</ListItem>
</List>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}
55. list-header-headref
55.0.1. List Header
The List Header component creates a list header, which can be used for grouping list items. To create a header for any child element of the list, include itemHeader prop with ListItem component. The List Header of NativeBase comes with default style which is easily customisable.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, List, ListItem, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class ListHeaderExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<List>
<ListItem itemHeader first>
<Text>COMEDY</Text>
</ListItem>
<ListItem >
<Text>Hangover</Text>
</ListItem>
<ListItem>
<Text>Horrible Bosses</Text>
</ListItem>
<ListItem last>
<Text>Conjuring</Text>
</ListItem>
<ListItem itemHeader>
<Text>ACTION</Text>
</ListItem>
<ListItem>
<Text>Terminator Genesis</Text>
</ListItem>
</List>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}56. list-icon-headref
56.0.1. List Icon
Lists can have icons assigned either to the left and/or right side of each list item.
Along with icons, list item can also have badges assigned.
To have note kind of text for list item, include note prop with Text component of ListItem.
![]()
![]()
Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, List, ListItem, Text, Icon, Left, Body, Right, Switch } from 'native-base';
export default class ListIconExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<List>
<ListItem icon>
<Left>
<Icon name="plane" />
</Left>
<Body>
<Text>Airplane Mode</Text>
</Body>
<Right>
<Switch value={false} />
</Right>
</ListItem>
<ListItem icon>
<Left>
<Icon name="wifi" />
</Left>
<Body>
<Text>Wi-Fi</Text>
</Body>
<Right>
<Text>GeekyAnts</Text>
<Icon name="arrow-forward" />
</Right>
</ListItem>
<ListItem icon>
<Left>
<Icon name="bluetooth" />
</Left>
<Body>
<Text>Bluetooth</Text>
</Body>
<Right>
<Text>On</Text>
<Icon name="arrow-forward" />
</Right>
</ListItem>
</List>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}
57. list-avatar-headref
57.0.1. List Avatar
List Avatars are medium to showcase an image with your list item whose dimension lays between icon and thumbnail. To create a avatar list, nest <Thumbnail> component within <ListItem> component.
![]()

Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, List, ListItem, Left, Body, Right, Thumbnail, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class ListAvatarExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<List>
<ListItem avatar>
<Left>
<Thumbnail source={{ uri: 'Image URL' }} />
</Left>
<Body>
<Text>Kumar Pratik</Text>
<Text note>Doing what you like will always keep you happy . .</Text>
</Body>
<Right>
<Text note>3:43 pm</Text>
</Right>
</ListItem>
</List>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}
58. list-thumbnail-headref
58.0.1. List Thumbnail
List Thumbnails are the medium to exhibit an image with your list item. To create a thumbnail list, nest <Thumbnail> component within <ListItem> component with few props and style.
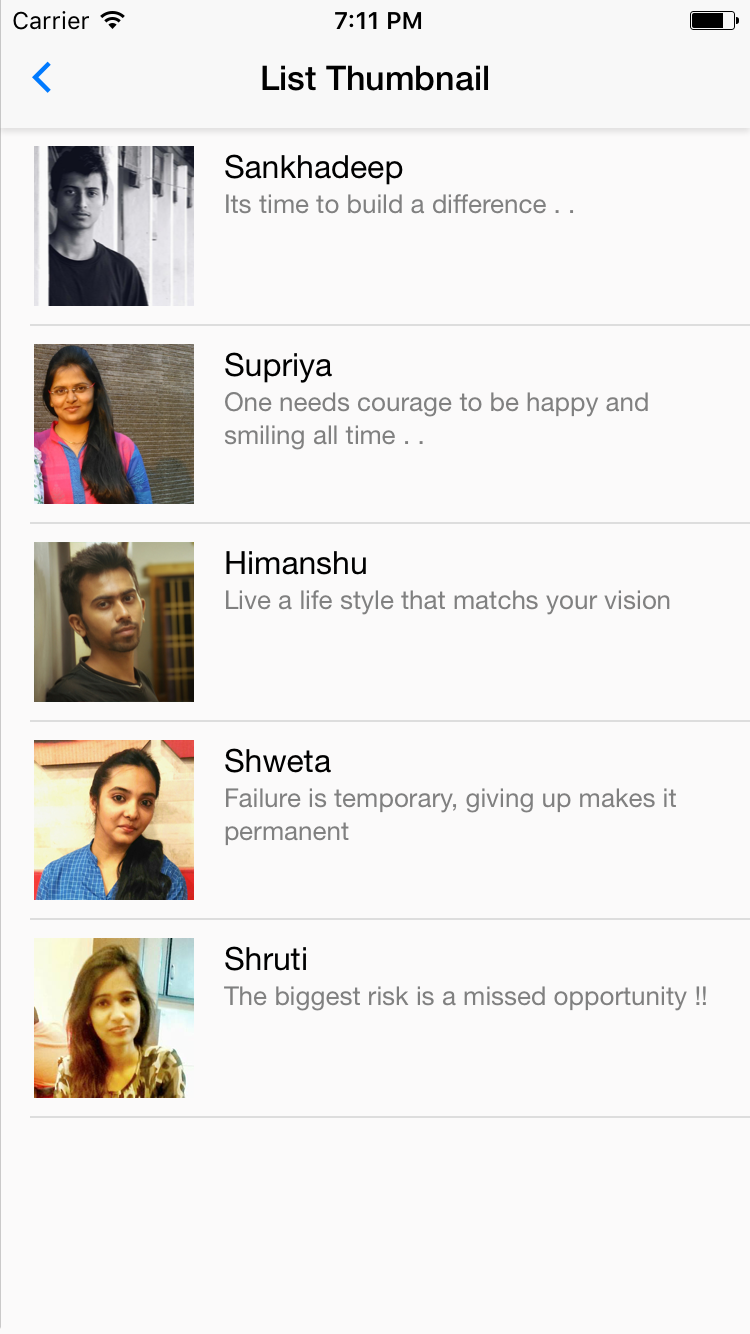
![]()
Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, List, ListItem, Thumbnail, Text, Body } from 'native-base';
export default class ListThumbnailExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<List>
<ListItem>
<Thumbnail square size={80} source={{ uri: 'Image URL' }} />
<Body>
<Text>Sankhadeep</Text>
<Text note>Its time to build a difference . .</Text>
</Body>
</ListItem>
</List>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}
59. dynamic-list-headref
59.0.1. Dynamic List
A center aspect designed for efficient representation of vertically scrolling lists of changing data. The simplest way is to create a List dataArray, populate it with an array of data chunks, and instantiate a ListItem component with that chunk of data and a renderRow callback which takes a chunk from the whole data array and returns a renderable component.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, List, ListItem, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class DynamicListExample extends Component {
render() {
var items = ['Simon Mignolet','Nathaniel Clyne','Dejan Lovren','Mama Sakho','Emre Can'];
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<List dataArray={items}
renderRow={(item) =>
<ListItem>
<Text>{item}</Text>
</ListItem>
}>
</List>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}
For more advanced implementation of rendering list dynamically, take a look at nativebase-tutorial.
60. list-seperator-headref
60.0.1. List Separator
Separator component is a separator usually used in list, which can be used for grouping list items. Though it is used with List, you can use it anywhere in your app.
Replacing Component: React Native View


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, List, ListItem, Text, Separator } from 'native-base';
export default class ListSeparatorExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Separator bordered>
<Text>FORWARD</Text>
</Separator>
<ListItem >
<Text>Aaron Bennet</Text>
</ListItem>
<ListItem>
<Text>Claire Barclay</Text>
</ListItem>
<ListItem last>
<Text>Kelso Brittany</Text>
</ListItem>
<Separator bordered>
<Text>MIDFIELD</Text>
</Separator>
<ListItem>
<Text>Caroline Aaron</Text>
</ListItem>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| bordered | - | - | adds border to top and bottom of the separator |
61. Picker
Renders the native picker component on iOS and Android.
Replacing Component: React Native Picker


Regular Syntax
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { Platform } from "react-native";
import {
Container,
Header,
Title,
Content,
Button,
Icon,
Text,
Right,
Body,
Left,
Picker,
Form,
View,
H3,
Item as FormItem
} from "native-base";
const Item = Picker.Item;
class RegularPicker extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
selected1: "key1"
};
}
onValueChange(value: string) {
this.setState({
selected1: value
});
}
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header>
<Left>
<Button transparent onPress={() => this.props.navigation.goBack()}>
<Icon name="arrow-back" />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body>
<Title>Regular</Title>
</Body>
<Right />
</Header>
<Content>
<Form>
<Picker
iosHeader="Select one"
mode="dropdown"
selectedValue={this.state.selected1}
onValueChange={this.onValueChange.bind(this)}
>
<Item label="Wallet" value="key0" />
<Item label="ATM Card" value="key1" />
<Item label="Debit Card" value="key2" />
<Item label="Credit Card" value="key3" />
<Item label="Net Banking" value="key4" />
</Picker>
</Form>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}
export default RegularPicker;
61.1. Advanced Pickers (iOS only)
61.1.1. Placeholder
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { Platform } from "react-native";
import {
Container,
Header,
Title,
Content,
Button,
Icon,
Text,
Right,
Body,
Left,
Picker,
Form,
View,
H3,
Item as FormItem
} from "native-base";
const Item = Picker.Item;
class RegularPicker extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
selected2: undefined
};
}
onValueChange2(value: string) {
this.setState({
selected2: value
});
}
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header>
<Left>
<Button transparent onPress={() => this.props.navigation.goBack()}>
<Icon name="arrow-back" />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body>
<Title>Placeholder Picker</Title>
</Body>
<Right />
</Header>
<Content>
<Form>
<Picker
mode="dropdown"
placeholder="Select One"
selectedValue={this.state.selected2}
onValueChange={this.onValueChange2.bind(this)}
>
<Item label="Wallet" value="key0" />
<Item label="ATM Card" value="key1" />
<Item label="Debit Card" value="key2" />
<Item label="Credit Card" value="key3" />
<Item label="Net Banking" value="key4" />
</Picker>
</Form>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}
export default RegularPicker;</code></pre>
61.1.2. Placeholder (without note)
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { Platform } from "react-native";
import {
Container,
Header,
Title,
Content,
Button,
Icon,
Text,
Right,
Body,
Left,
Picker,
Form,
View,
H3,
Item as FormItem
} from "native-base";
const Item = Picker.Item;
class RegularPicker extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
selected2: undefined
};
}
onValueChange2(value: string) {
this.setState({
selected2: value
});
}
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header>
<Left>
<Button transparent onPress={() => this.props.navigation.goBack()}>
<Icon name="arrow-back" />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body>
<Title>Placeholder picker 2</Title>
</Body>
<Right />
</Header>
<Content>
<Form>
<Picker
mode="dropdown"
placeholder="Select One"
note={false}
selectedValue={this.state.selected2}
onValueChange={this.onValueChange2.bind(this)}
>
<Item label="Wallet" value="key0" />
<Item label="ATM Card" value="key1" />
<Item label="Debit Card" value="key2" />
<Item label="Credit Card" value="key3" />
<Item label="Net Banking" value="key4" />
</Picker>
</Form>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}
export default RegularPicker;
61.1.3. Custom Back Button
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { Platform } from "react-native";
import {
Container,
Header,
Title,
Content,
Button,
Icon,
Text,
Right,
Body,
Left,
Picker,
Form,
View,
H3,
Item as FormItem
} from "native-base";
const Item = Picker.Item;
class RegularPicker extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
selected3: "key3"
};
}
onValueChange3(value: string) {
this.setState({
selected3: value
});
}
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header>
<Left>
<Button transparent onPress={() => this.props.navigation.goBack()}>
<Icon name="arrow-back" />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body>
<Title>Custom back button</Title>
</Body>
<Right />
</Header>
<Content>
<Form>
<Picker
mode="dropdown"
headerBackButtonText="Baaack!"
selectedValue={this.state.selected3}
onValueChange={this.onValueChange3.bind(this)}
>
<Item label="Wallet" value="key0" />
<Item label="ATM Card" value="key1" />
<Item label="Debit Card" value="key2" />
<Item label="Credit Card" value="key3" />
<Item label="Net Banking" value="key4" />
</Picker>
</Form>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}
export default RegularPicker;
61.1.4. Custom Header Text
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { Platform } from "react-native";
import {
Container,
Header,
Title,
Content,
Button,
Icon,
Text,
Right,
Body,
Left,
Picker,
Form,
View,
H3,
Item as FormItem
} from "native-base";
const Item = Picker.Item;
class RegularPicker extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
selected3: "key3"
};
}
onValueChange3(value: string) {
this.setState({
selected3: value
});
}
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header>
<Left>
<Button transparent onPress={() => this.props.navigation.goBack()}>
<Icon name="arrow-back" />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body>
<Title>Custom back button</Title>
</Body>
<Right />
</Header>
<Content>
<Form>
<Picker
mode="dropdown"
iosHeader="Your Header"
selectedValue={this.state.selected3}
onValueChange={this.onValueChange3.bind(this)}
>
<Item label="Wallet" value="key0" />
<Item label="ATM Card" value="key1" />
<Item label="Debit Card" value="key2" />
<Item label="Credit Card" value="key3" />
<Item label="Net Banking" value="key4" />
</Picker>
</Form>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}
export default RegularPicker;
61.1.5. Custom Header Style
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { Platform } from "react-native";
import {
Container,
Header,
Title,
Content,
Button,
Icon,
Text,
Right,
Body,
Left,
Picker,
Form,
View,
H3,
Item as FormItem
} from "native-base";
const Item = Picker.Item;
class RegularPicker extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
selected5: "key2"
};
}
onValueChange5(value: string) {
this.setState({
selected5: value
});
}
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header>
<Left>
<Button transparent onPress={() => this.props.navigation.goBack()}>
<Icon name="arrow-back" />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body>
<Title>Cutom Header Style</Title>
</Body>
<Right />
</Header>
<Content>
<Form>
<Picker
mode="dropdown"
headerStyle={{ backgroundColor: "#b95dd3" }}
headerBackButtonTextStyle={{ color: "#fff" }}
headerTitleStyle={{ color: "#fff" }}
selectedValue={this.state.selected5}
onValueChange={this.onValueChange5.bind(this)}
>
<Item label="Wallet" value="key0" />
<Item label="ATM Card" value="key1" />
<Item label="Debit Card" value="key2" />
<Item label="Credit Card" value="key3" />
<Item label="Net Banking" value="key4" />
</Picker>
</Form>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}
export default RegularPicker;
61.1.6. Custom Header
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { Platform } from "react-native";
import {
Container,
Header,
Title,
Content,
Button,
Icon,
Text,
Right,
Body,
Left,
Picker,
Form,
View,
H3,
Item as FormItem
} from "native-base";
const Item = Picker.Item;
class RegularPicker extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
selected1: "key1"
};
}
onValueChange(value: string) {
this.setState({
selected1: value
});
}
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header>
<Left>
<Button transparent onPress={() => this.props.navigation.goBack()}>
<Icon name="arrow-back" />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body style={{ flex: 3 }}>
<Title>Custom Header</Title>
</Body>
<Right />
</Header>
<Content>
<Form>
<Picker
renderHeader={backAction =>
<Header style={{ backgroundColor: "#f44242" }}>
<Left>
<Button transparent onPress={backAction}>
<Icon name="arrow-back" style={{ color: "#fff" }} />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body style={{ flex: 3 }}>
<Title style={{ color: "#fff" }}>Your Header</Title>
</Body>
<Right />
</Header>}
mode="dropdown"
style={{ width: Platform.OS === "ios" ? undefined : 200 }}
selectedValue={this.state.selected1}
onValueChange={this.onValueChange.bind(this)}
>
<Item label="Wallet" value="key0" />
<Item label="ATM Card" value="key1" />
<Item label="Debit Card" value="key2" />
<Item label="Credit Card" value="key3" />
<Item label="Net Banking" value="key4" />
</Picker>
</Form>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}
export default RegularPicker;
Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| renderHeader | - | - | akes component that appears as header of the Picker, comes with a backAction prop to close the picker. Like renderHeader={(backAction) =>{ // BODY } |
| headerStyle | - | - | Custom style to be given to Header |
| placeholder | - | - | Default placeholder when no value is selected. |
| iosHeader | - | - | Custom text for the header title. |
| headerBackButtonText | - | - | Custom text for the header back button. |
| textStyle | - | - | Text style of header |
| itemStyle | - | - | Style of items in the Picker |
| headerStyle | - | - | Style of header. |
| headerStyle | - | - | Style of header. |
| itemTextStyle | - | - | Text style of item component in Picker |
| supportedOrientations | - | Portrait, Landscape, Landscape-left, Landscape-right | Allows the modal to be rotated to any of the specified orientations |
| headerBackButtonText | "Back" | user-defined text | Used for custom backButton text |
| placeholder | - | Strings | Pass placeholder for Picker component |
62. radio-button-headref
63. Radio Button
Radio buttons let the user select any one from a set of options.
Replacing Component: React Native TouchableOpacity


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, ListItem, Text, Radio, Right } from 'native-base';
export default class RadioButtonExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<ListItem>
<Text>Daily Stand Up</Text>
<Right>
<Radio selected={false} />
</Right>
</ListItem>
<ListItem>
<Text>Discussion with Client</Text>
<Right>
<Radio selected={true} />
</Right>
</ListItem>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| selected | false | boolean | Represents the state value of an item from set of choices. |
64. search-bar-headref
65. Search Bar
It’s kind of common on the Internet where – if we fail to get what we are looking for on a website, we resort to searching. Search box has always been an essential part of any application.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Header, Item, Input, Icon, Button, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class SearchBarExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header searchBar rounded>
<Item>
<Icon name="ios-search" />
<Input placeholder="Search" />
<Icon name="ios-people" />
</Item>
<Button transparent>
<Text>Search</Text>
</Button>
</Header>
</Container>
);
}
}searchBar: Prop to be used with<Header>component to have Search bar onto the Header section of your screen.- Replacing Component: React Native View
Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| rounded | regular | - | Wraps the search bar with predefined border options. |
66. Segment
Segments are best used as an alternative for tabs. Mainly used in iOS.


Syntax (basic)
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Header, Left, Body, Right, Button, Icon, Segment, Content, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class SegmentExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header>
<Left>
<Button transparent>
<Icon name="arrow-back" />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body>
<Segment>
<Button first><Text>Puppies</Text></Button>
<Button last active><Text>Cubs</Text></Button>
</Segment>
</Body>
<Right>
<Button transparent>
<Icon name="search" />
</Button>
</Right>
</Header>
<Content padder>
<Text>Awesome segment</Text>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}Segment takes Button as children. The active Button shoud be given an active prop (implementation is totally up to you).
Also the first and last buttons should be given props first and last respectively.
Pro tip: It is advisable to use hasSegment prop with Header if you're using Segment below the header.
Syntax (Outside Header)
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Header, Left, Body, Right, Button, Icon, Title, Segment, Content, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class SegementOutsideHeaderExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header hasTabs>
<Left>
<Button transparent>
<Icon name="arrow-back" />
</Button>
</Left>
<Body>
<Title>Hello</Title>
</Body>
<Right>
<Button transparent>
<Icon name="search" />
</Button>
</Right>
</Header>
<Segment>
<Button first>
<Text>Puppies</Text>
</Button>
<Button>
<Text>Kittens</Text>
</Button>
<Button last active>
<Text>Cubs</Text>
</Button>
</Segment>
<Content padder>
<Text>Awesome segment</Text>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}67. Spinner
If you have certain screens of your app that take some time to load, you may want to consider a page loader. A page loader is any kind of animation that visually communicates to a visitor that the page is loading and to just sit tight for a few seconds. Without a page loader, user might think that the app is being unresponsive and just click away in frustration. A page loader also provides a small distraction which can actually makes the wait seem much shorter.
Replacing Component: React Native ActivityIndicator


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Spinner } from 'native-base';
export default class SpinnerExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Spinner />
<Spinner color='red' />
<Spinner color='green' />
<Spinner color='blue' />
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| color | #45D56E | user-defined | Color of Spinner |
68. tabs-def-headref
69. Tabs
Tabs are a horizontal region of buttons or links that allow for a consistent navigation experience between screens. It can contain any combination of text and icons, and is a popular method for enabling mobile navigation.
Replacing Component: react-native-scrollable-tab-view <ScrollableTabView>




Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Header, Content, Tab, Tabs } from 'native-base';
import Tab1 from './tabOne';
import Tab2 from './tabTwo';
export default class TabsExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header hasTabs />
<Tabs initialPage={1}>
<Tab heading="Tab1">
<Tab1 />
</Tab>
<Tab heading="Tab2">
<Tab2 />
</Tab>
<Tab heading="Tab3">
<Tab3 />
</Tab>
</Tabs>
</Container>
);
}
}Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| locked | false | boolean | Disable swipe |
| initialPage | - | integer | Set default active tab |
| tabBarPosition | top | top, bottom, overlayTop, overlayBottom | Set position of Tabs |
Known Issues : Custom tabHeading is not yet supported for
ScrollableTab heading only accepts a string. Pro-Tip : It is advisable to use
hasTabs prop with Header while using Tabs. 70. advanced-tabs-headref
70.0.1. Advanced Tabs
Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Header, Tab, Tabs, TabHeading, Icon, Text } from 'native-base';
import Tab1 from './tabOne';
import Tab2 from './tabTwo';
export default class AdvancedTabsExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header hasTabs/>
<Tabs>
<Tab heading={ <TabHeading><Icon name="camera" /><Text>Camera</Text></TabHeading>}>
<Tab1 />
</Tab>
<Tab heading={ <TabHeading><Text>No Icon</Text></TabHeading>}>
<Tab2 />
</Tab>
<Tab heading={ <TabHeading><Icon name="apps" /></TabHeading>}>
<Tab3 />
</Tab>
</Tabs>
</Container>
);
}
}Syntax (scrollable)
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Tab, Tabs } from 'native-base';
import Tab1 from './tabOne';
import Tab2 from './tabTwo';
export default class TabsExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Header hasTabs/>
<Tabs renderTabBar={()=> <ScrollableTab />}>
<Tab heading="Tab1">
<Tab1 />
</Tab>
<Tab heading="Tab2">
<Tab2 />
</Tab>
<Tab heading="Tab3">
<Tab3 />
</Tab>
<Tab heading="Tab4">
<Tab4 />
</Tab>
<Tab heading="Tab5">
<Tab5 />
</Tab>
</Tabs>
</Container>
);
}
}| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| heading | - | string, |
Label String, or Component |
| tabStyle | - | style object | Style for tab bar |
| activeTabStyle | - | style object | Style for active tab bar |
| textStyle | - | style object | Style for text |
| activeTextStyle | - | style object | Style for active text |
71. Thumbnail
Thumbnail component works very similar to Image. It helps you to showcase an image with variuos dimensions and shapes. By default, Thumbnail renders an image in circular shape.
Replacing Component: React Native Image


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Thumbnail, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class ThumbnailExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Text>Square Thumbnail</Text>
<Thumbnail square source={{uri: 'Image URL'}} />
<Thumbnail square small source={{uri: 'Image URL'}} />
<Text>Circular Thumbnail</Text>
<Thumbnail source={{uri: 'Image URL'}} />
<Thumbnail large source={{uri: 'Image URL'}} />
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| source | - | - | Image path for thumbnail. |
| square | - | - |
Represents shape of thumbnail. By default thumbnail is circle in shape. |
| small | - | - | Small thumbnail with width and height of 40px. |
| large | - | - | Large thumbnail with width and height of 80px. |
72. Toast
NativeBase Toast can be used to display quick warning or error messages.
For Toast to work, you need to wrap your topmost component inside <Root> from native-base.
import { Root } from "native-base";
import { StackNavigator } from "react-navigation";
const AppNavigator = StackNavigator(
{
Page: { screen: Page },
}
);
export default () =>
<Root>
<AppNavigator />
</Root>;


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Toast, Button, Text, Icon } from 'native-base';
export default class Toast extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
showToast: false
}
}
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content padder>
<Button onPress={()=> Toast.show({
text: 'Wrong password!',
position: 'bottom',
buttonText: 'Okay'
})}>
<Text>Toast</Text>
</Button>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}Configuration
| Key | Value | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| text | - | string | The text content to be shown in the toast. |
| buttonText | - | string | The text to be displayed inside the button. |
| position | bottom | top, bottom, center | Sets position for the toast. |
| type | - | danger,success,warning | Sets context to the Toast. |
| duration | - | integer | Milliseconds after which Toast disappers |
73. Typography
NativeBase provides you with the Heading Tags, namely H1, H2 and H3 components. These Heading tags helps you prioritize the content of your screen.
Replacing Component for H1, H2, H3, Text: React Native Text


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, H1, H2, H3, Text } from 'native-base';
export default class TypographyExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<H1>Header One</H1>
<H2>Header Two</H2>
<H3>Header Three</H3>
<Text>Default</Text>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}Configuration
| Property | Default | Option | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | font-size: 27 | user-defined | Heading tag <H1> |
| H2 | font-size: 24 | user-defined | Heading tag <H2> |
| H3 | font-size: 21 | user-defined | Heading tag <H3> |
74. Drawer
Drawer for both iOS and Android.
Drawer can be the perfect option to provide navigation options.


Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Drawer } from 'native-base';
import SideBar from './yourPathToSideBar';
export default class DrawerExample extends Component {
render() {
closeDrawer = () => {
this.drawer._root.close()
};
openDrawer = () => {
this.drawer._root.open()
};
return (
<Drawer
ref={(ref) => { this.drawer = ref; }}
content={<SideBar navigator={this.navigator} />}
onClose={() => this.closeDrawer()} >
// Main View
</Drawer>
);
}
}Note: You need to create your own SideBar component and import it.
75. ref-components-headref
76. Ref to Components
- NativeBase is built on top of React Native. Hence, the components of NativeBase have respective replacing React Native elements.
- NativeBase has now made it easy for developers, to access the any of its components using ref, along with its associated React Native elements.
- After building your component, you may find yourself wanting to reach out and invoke methods on component instances returned from render().
- This can be achieved from refs. Refs are a great way to send a message to a particular child instance.
- The ref attribute takes a callback function, and the callback will be executed immediately after the component is mounted or unmounted.
Syntax
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { Container, Content, Button } from 'native-base';
export default class RefExample extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Container>
<Content>
<Button ref={ (c) => this._button = c }>
Click Me
</Button>
</Content>
</Container>
);
}
}this._buttongets you the reference of NativeBase Button.this._button._rootgets you the reference of NativeBase Button's replacing React Native element i.e., TouchableOpacity.- This feature is accessible with all of NativeBase components.